Mouse over the small images above to change larger image and associated description. (Alternatively, read static PDF.)
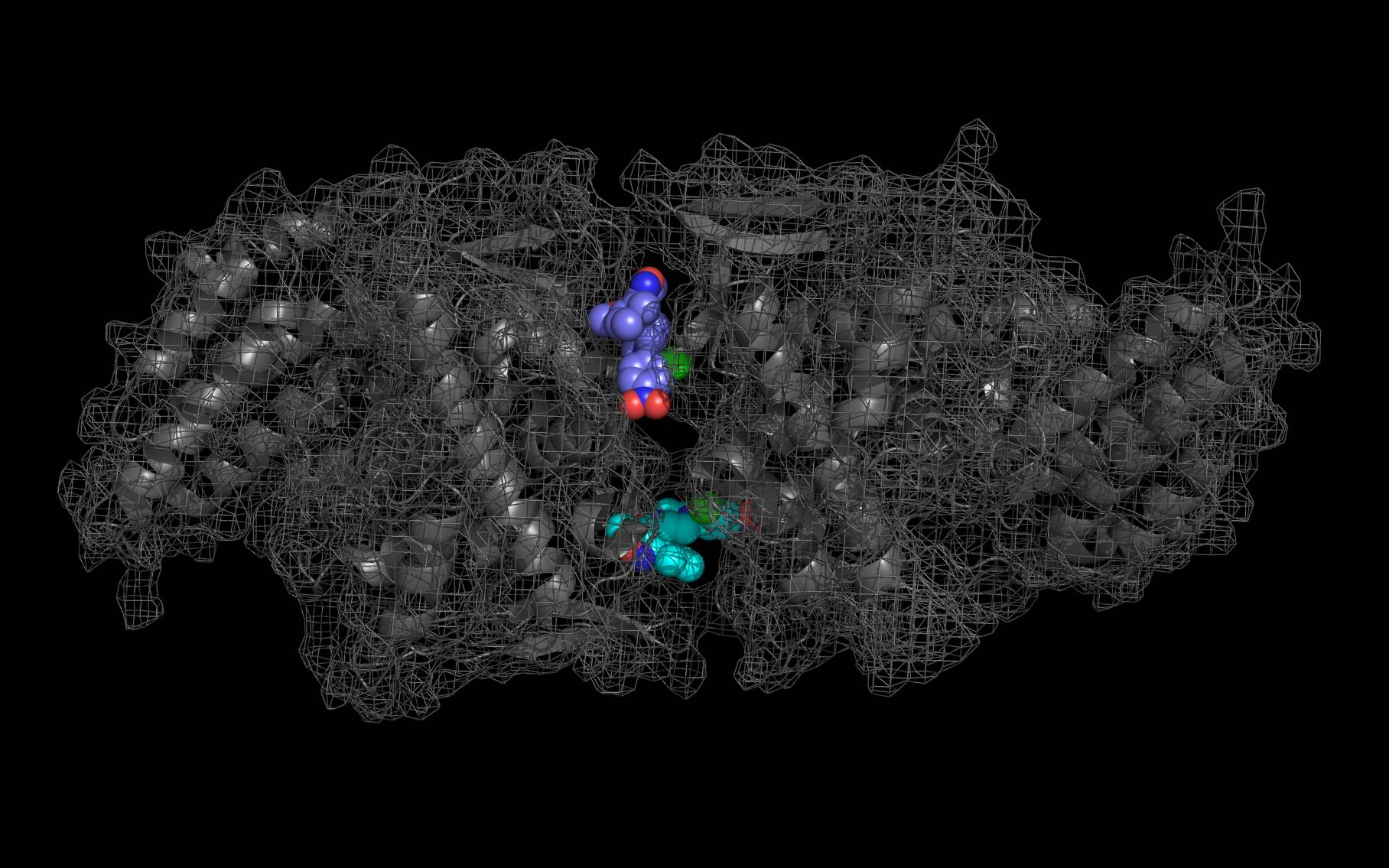
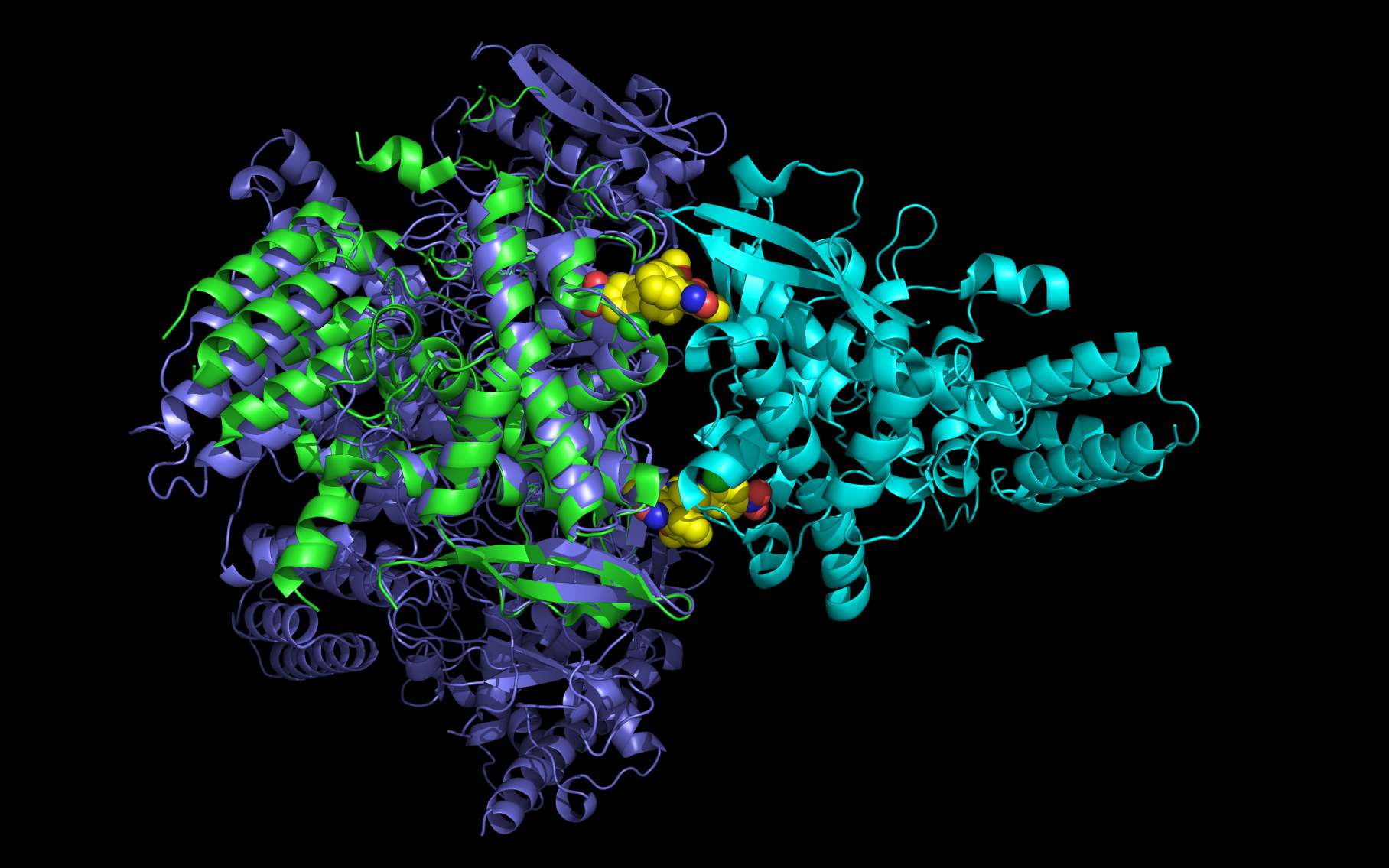
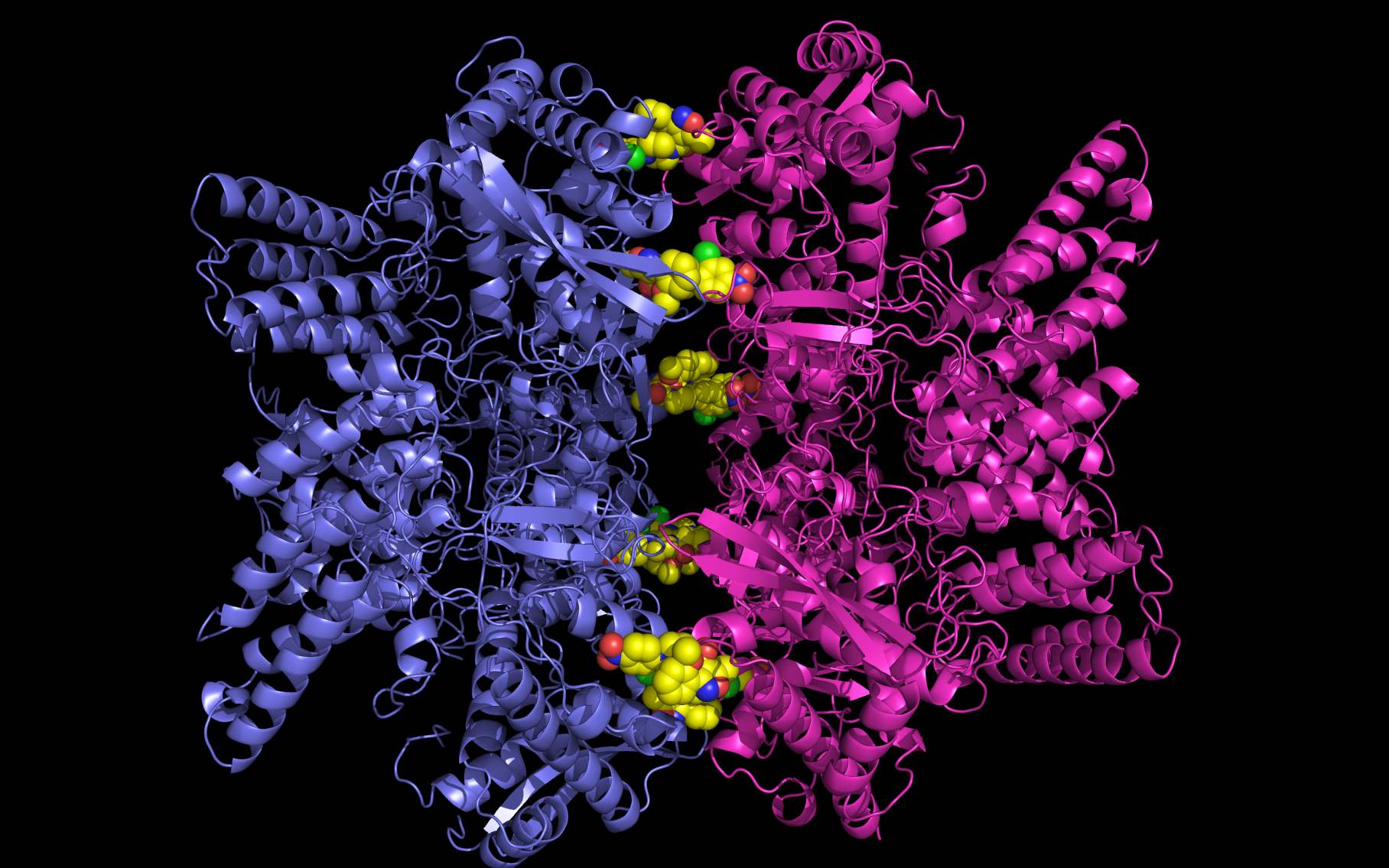
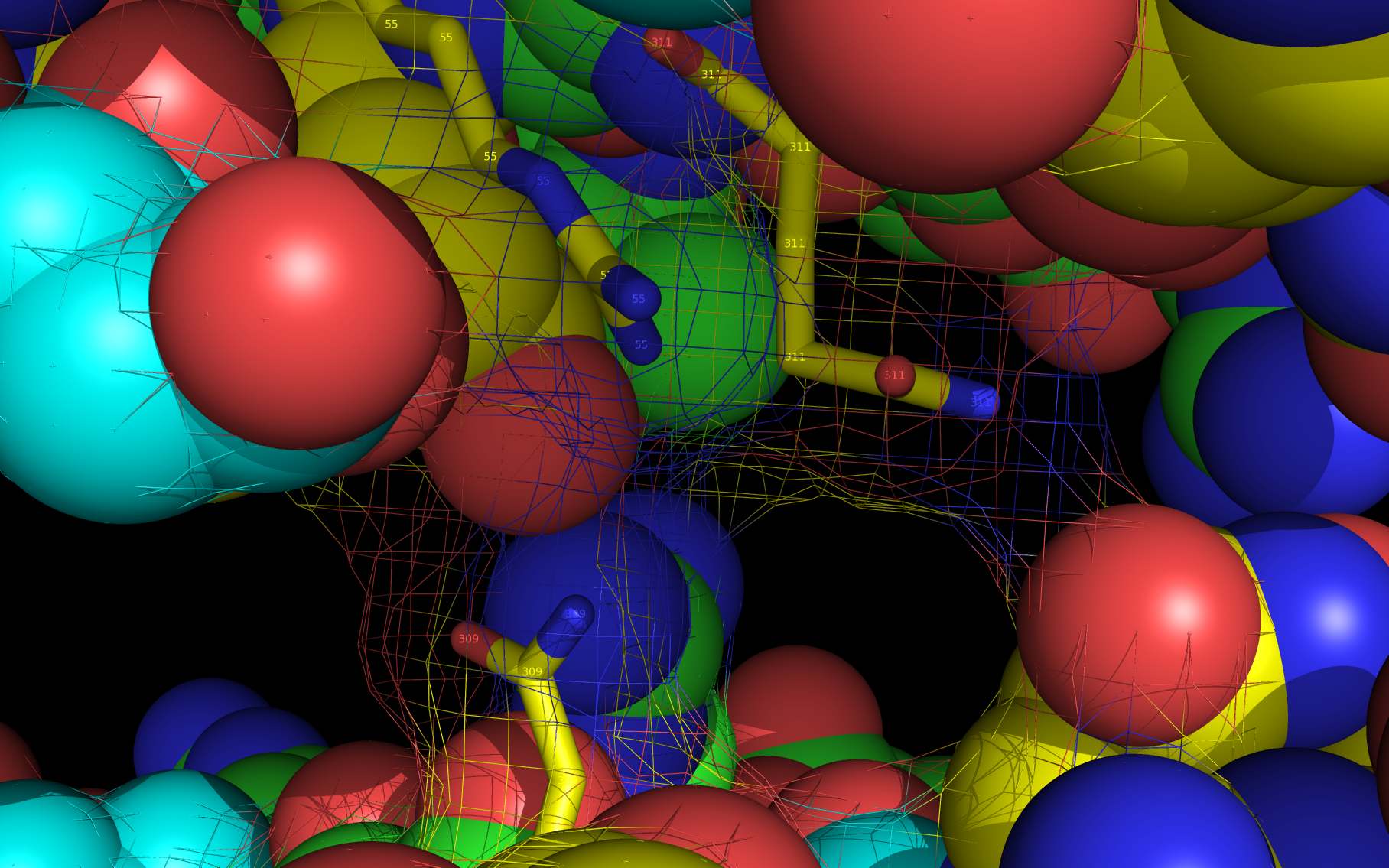
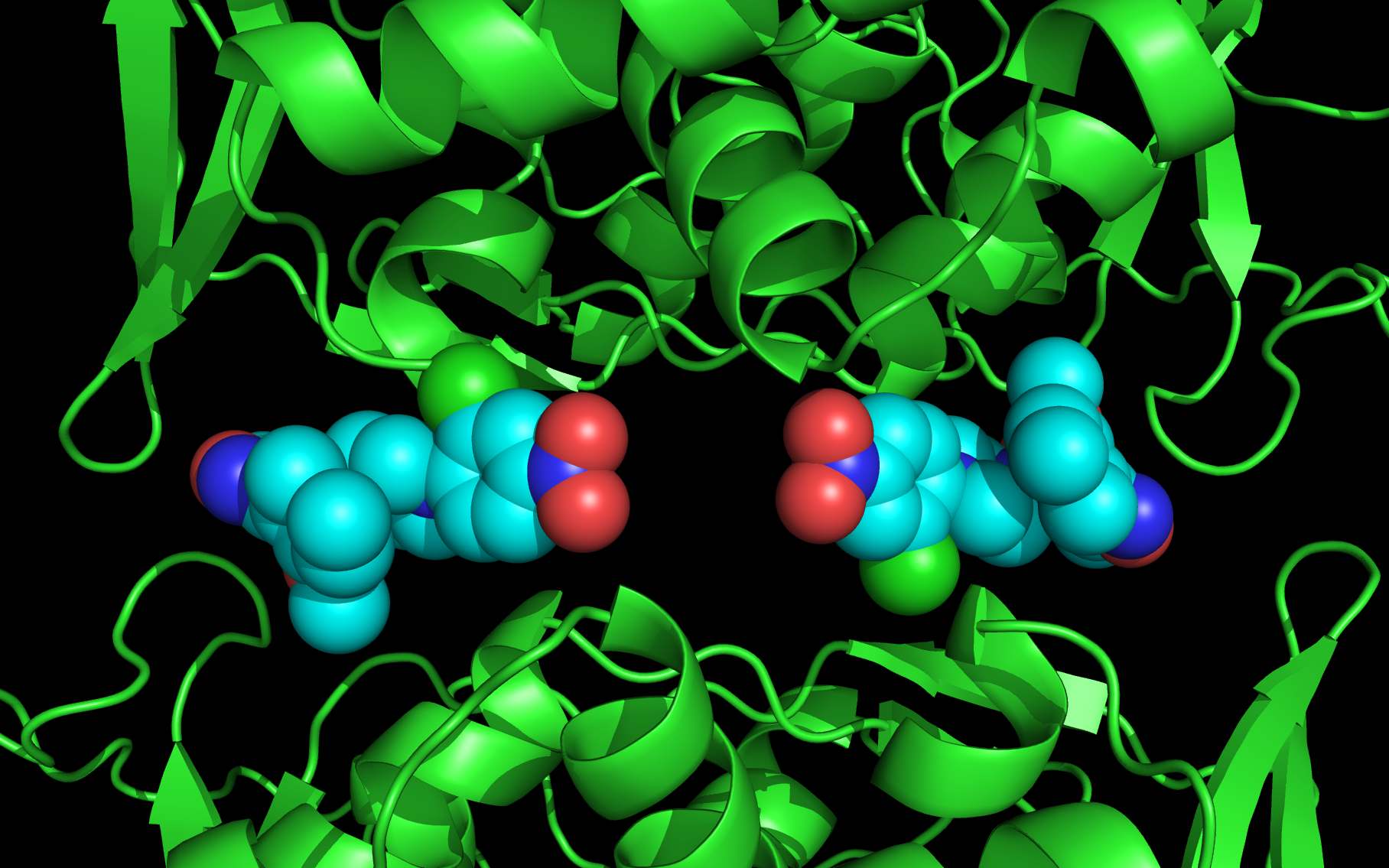
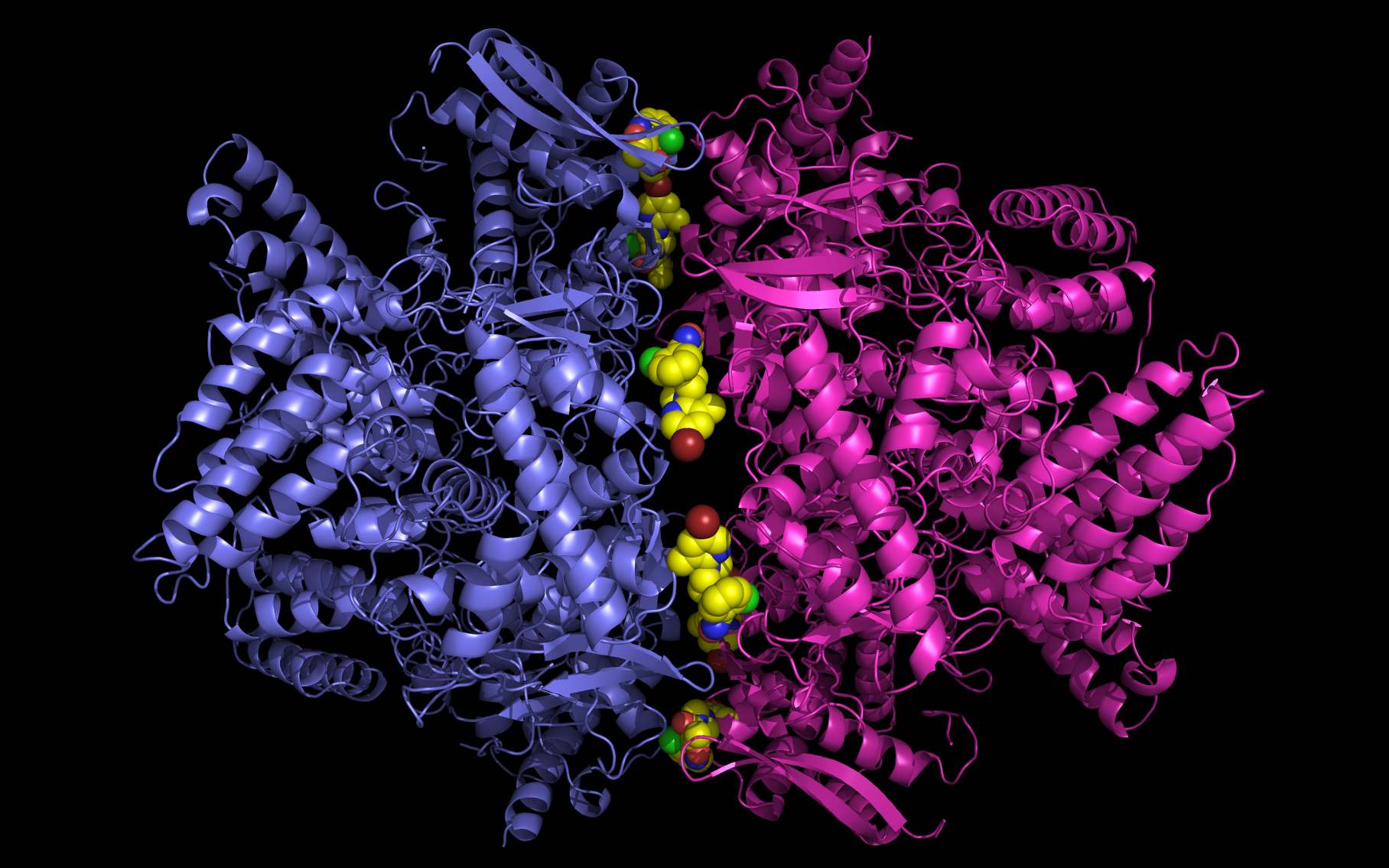
Shown above are two monomers of LGH: one LGH is shown bound to two nucleoprotein monomers ( grey mesh and cartoon ) in the reported crystallographic position (bottom LGH with cyan carbon spheres ) and one LGH in shown bound in the wwavePDB-identified putative alternative binding position (top LGH with purple carbon spheres ).
The following pictures and description document the finding and building of an alternative binding site for a class of influenza A nucleoprotein binding compounds that have been examined as drug candidates1,2,3. Kao et al.1 were the first to discover that a small molecule compound, nucleozin, triggered the aggregation of nucleoprotein, inhibited its nuclear accumulation with nanomolar effectiveness, protected mice against lethal challenges of H5N1, and produced a mutation in the nucleoprotein, Y289H, conferring resistance to nucleozin. Su et al.2 identified a number of small molecule compounds that also protected against lethal challenges but also induced resistance mutations. Su et al.2 found that nucleozin related compound, 3061, induced nucleoprotein aggregation and produced the nucleoprotein mutation Y52H. Gerritz at al.3 subsequently also reported nucleoprotein aggregation induced by additional nucleozin-related compounds and associated induced mutations. Nucleoproteins were co-crystallized with several compounds (BMS-8859865, BMS-8835596, BMS-8858387, BMS-8317808, and LGH4) and the x-ray structures were reported. The crystallized compounds were reported to bridge between monomers with the long axis of the compound positioned orthogonally to the plane of the nucleoprotein monomer-monomer interface. The long axis of superimposed nucleozin, compound 3061, and the crystallized compounds in the wwavePDB-identified alternative binding site is oriented in the the plane between the nucleoprotein monomers. In the process of using wwavePDB to look for on-target and off-target binding sites for this class of compounds, alternative putative binding sites for this class of compounds were identified. LGH in the crystal structure orientation and LGH in the alternative wwavePDB-identified binding site are shown above, relative to the plane of the dimer-dimer interface.
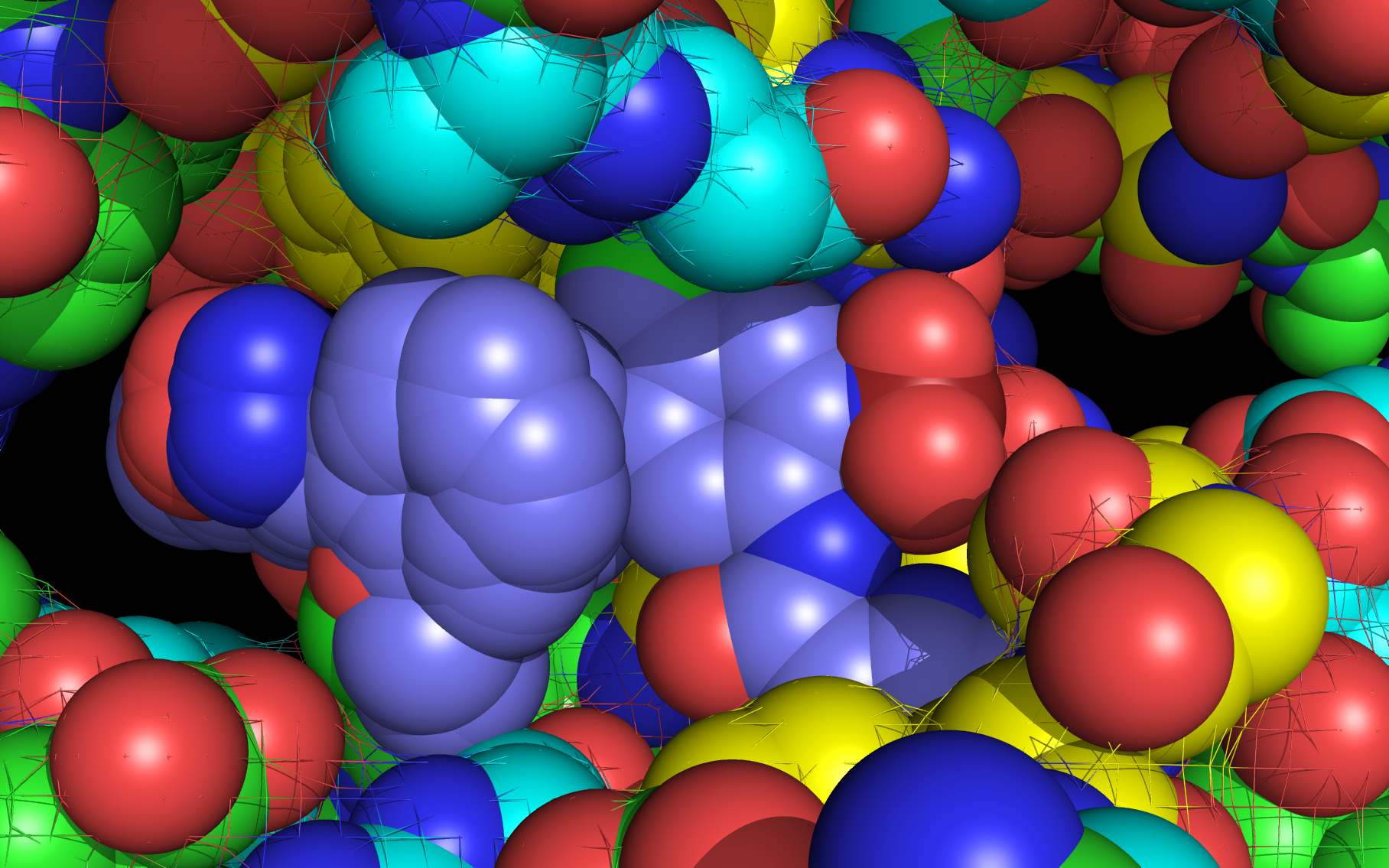
An alternative on-target nucleoprotein binding site identified by wwavePDB has features consistent with binding this class of compounds and the reported mutant data1,2,3. The wwavePDB-identified putative on-target nucleoprotein binding site has favorable stereochemistry. The wwavePDB-identified binding site is positioned along the interface between nucleoprotein trimers. The wwavePDB-identified binding site resides in a position that is roughly 90 degrees rotated and slightly shifted from the configuration reported in the crystal structures4,5,6,7,8. wwavePDB used the crystal structure9 of a nucleoprotein trimer (with no compound bound and with a R416A mutation) to build WWaveCores for a trimer-trimer interface. The WWaveCores defining the binding sites for the compounds (nucleozin1, compound 30612, BMS-8859865, BMS-8835596, BMS-8858387, BMS-8317808, and LGH4) were built by maintaining the trimer structure with the exception that three residue side chains were moved. The wwavePDB-identified putative alternative binding sites supplies detail that is consistent with, and may be important for, the interpretation of the reported mutant data1,2,3. Alternative wwavePDB-identified binding sites, whether for nucleozin or non-nucleozin related compounds, may represent new, well-defined, putative targets for nucleoprotein drug design. This example shows the utility of wwavePDB in finding and building alternative on-target binding sites for drug candidates that can be tested.
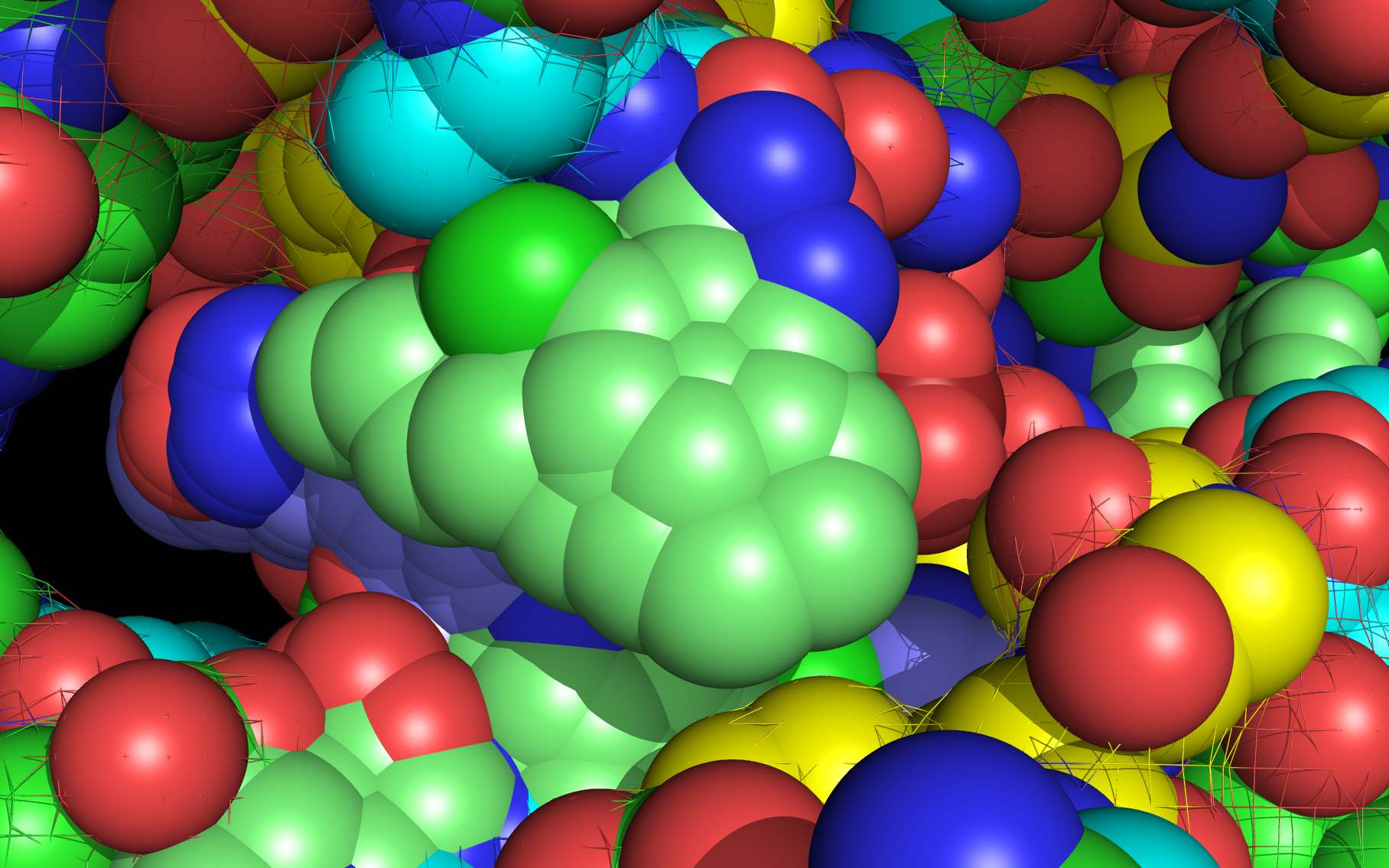
3RO54 nucleoprotein dimer cartoon and surface mesh is colored grey .
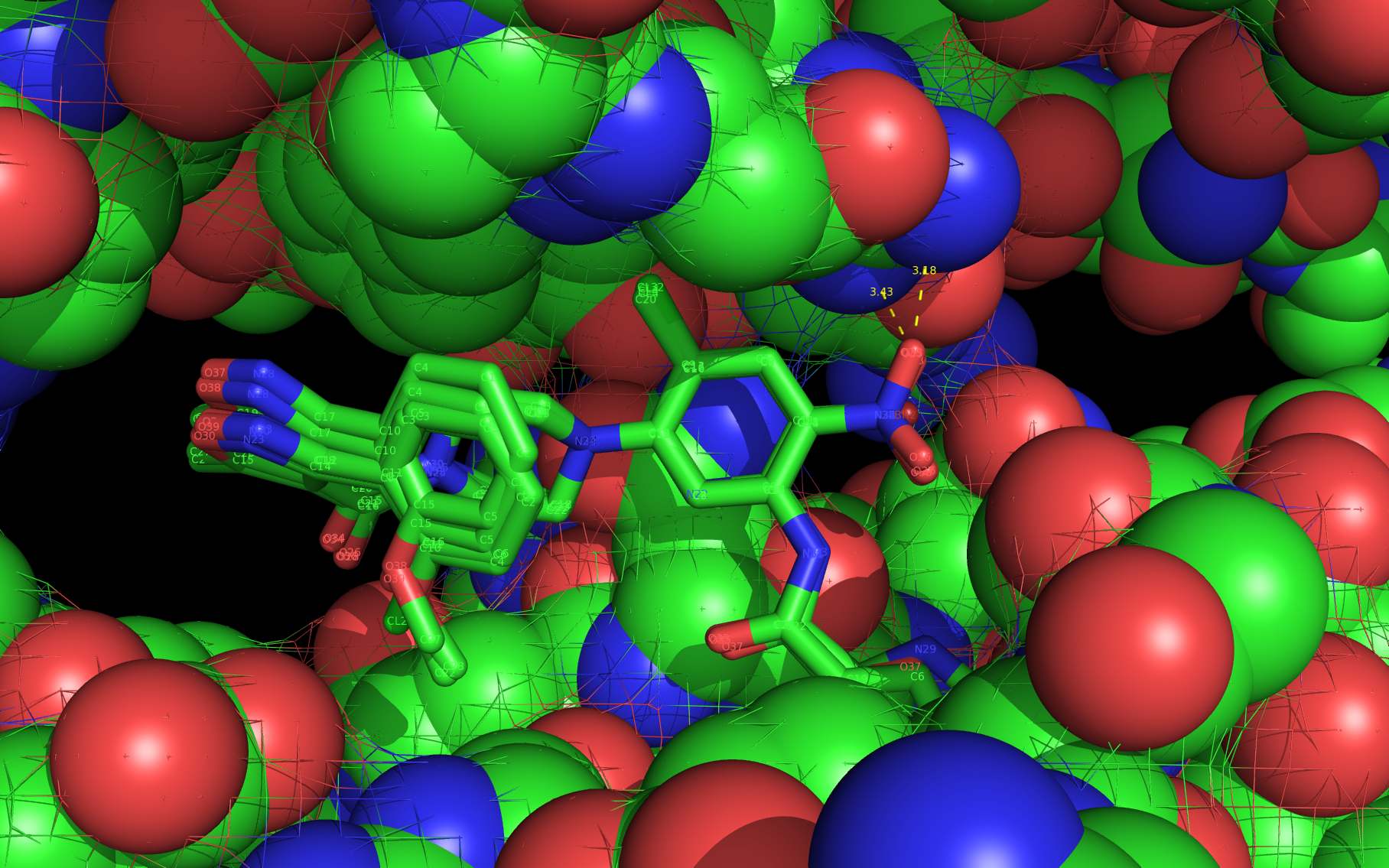
LGH molecule spheres oriented as in 3RO54 are color-coded according to element ( C N O Cl ).
LGH molecule spheres reoriented by twwistPDB into WWaveCores are color-coded according to element ( C N O Cl ).
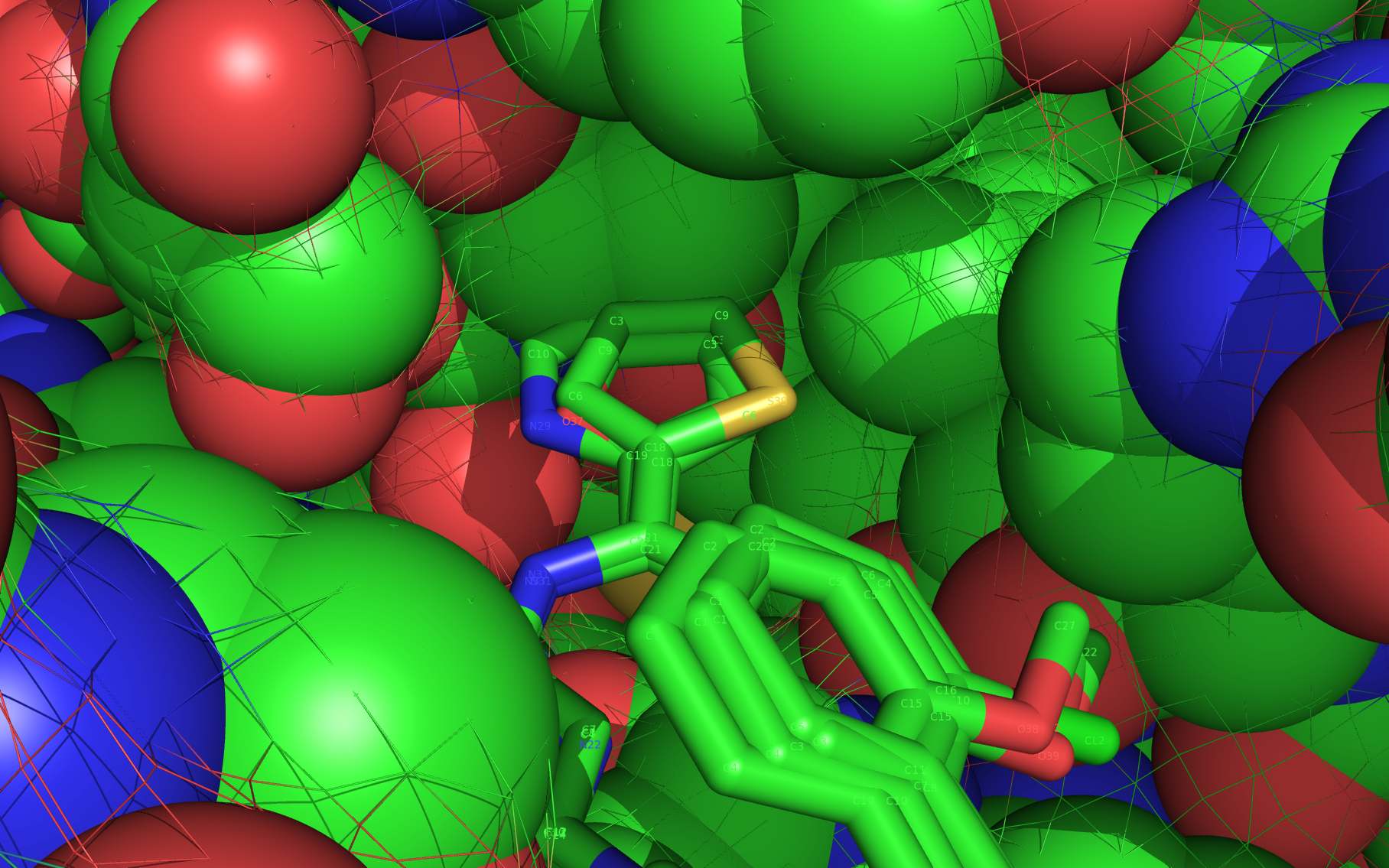
Nucleoprotein binding compounds
(The highlighted colors of the following SMILES match structures on the nucleoprotein binding compounds page)
nucleozin
CAS Number: 341001-38-5
IUPAC Name: [4-(2-chloro-4-nitrophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]
-(5-methyl-3-phenyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl)methanone
SMILES: c1ccccc1c2noc(C)c2C(=O)N3CCN(CC3)c4ccc(cc4Cl)[N+](=O)[O-]
3061 (also named “FA-2”)
IUPAC Name: 3-[3-[5-[5-(4,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl)
oxy-4-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]
oxy-4-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-14-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl
-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,15,16,17-tetradecahydrocyclopenta[a]
phenanthren-17-yl]-2H-furan-5-one
SMILES: Clc1ccccc1c2noc(C)c2C(=O)N3CCN(CC3)c4ccc(cc4Cl)[N+](=O)[O-]
LGH
IUPAC Name: [4-(2-chloro-4-nitrophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]
-[3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]methanone
SMILES: COc1ccccc1c2noc(C)c2C(=O)N3CCN(CC3)c4ccc(cc4Cl)[N+](=O)[O-]
BMS-831780 (also named “0MS”)
IUPAC Name: [4-(5-bromo-3-methylpyridin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl]
-[3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]methanone
SMILES: Clc1ccccc1c2noc(C)c2C(=O)N3CCN(CC3)c4c(C)cc(Br)cn4
BMS-883559 (also named “0MH”)
IUPAC Name: N-[4-chloro-5-[4-[3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazole-4-carbonyl]
piperazin-1-yl]-2-nitrophenyl]thiophene-2-carboxamide
SMILES: COc1ccccc1c2noc(C)c2C(=O)N3CCN(CC3)c4cc(NC(=O)c5sccc5)c(cc4Cl)[N+](=O)[O-]
BMS-885986 (also named “0MF”)
IUPAC Name: N-[4-chloranyl-5-[4-[[3-(2-methoxyphenyl)
-5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]carbonyl]
piperazin-1-yl]-2-nitro-phenyl]furan-2-carboxamide
SMILES: COc1ccccc1c2noc(C)c2C(=O)N3CCN(CC3)c4cc(NC(=O)c5occc5)c(cc4Cl)[N+](=O)[O-]
BMS-885838 (also named “0MR”)
IUPAC Name: N-[4-chloro-5-[4-[3-(2-methoxyphenyl)
-5-methyl-1,2-oxazole-4-carbonyl]
piperazin-1-yl]-2-nitrophenyl]pyridine-2-carboxamide
SMILES: COc1ccccc1c2noc(C)c2C(=O)N3CCN(CC3)c4cc(NC(=O)c5ncccc5)c(cc4Cl)[N+](=O)[O-]
1 Kao, R.Y.; Yang, D.; Lau, L.S.; Tsui, W.H.; Hu, L.; Dai, J.; Chan, M.P.; Chan, C.M.;
Wang, P.; Zheng, B.J.; Sun, J.; Huang, J.D.; Madar, J.; Chen, G.; Chen, H.;
Guan, Y.; Yuen, K.Y.;
“Identification of influenza A nucleoprotein as an antiviral target.”
Nat.Biotechnol. (2011) Jun;28;(6) 600-605
2 Su, C.Y.; Cheng, T.J.; Lin, M.I.; Wang, S.Y.; Huang, W.I.; Lin-Chu, S.Y.; Chen, Y.H.;
Wu, C.Y.; Lai, M.M.; Cheng, W.C.; Wu, Y.T.; Tsai, M.D.; Cheng, Y.S.; Wong, C.H.;
“High-throughput identification of compounds targeting influenza
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity.”
Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA (2010) Nov 9;107(45): 19151-19156
3 Gerritz, S.W.; Cianci, C.; Kim, S.; Pearce, B.C.; Deminie, C.; Discotto, L.;
McAuliffe, B.; Minassian, B.F.; Shi,S.; Zhu, S.; Zhai, W.; Pendri, A.; Li, G.;
Poss, M.A.; Edavettal, S.; McDonnell, P.A.; Lewis, H.A.; Maskos, K.; Mörtl, M.;
Kiefersauer, R.; Steinbacher, S.; Baldwin, E.T.; Metzler, W.; Bryson, J.;
Healy, M.D.; Philip, T.; Zoeckler, M.; Schartman, R.; Sinz, M.; Leyva-Grado, V.H.;
Hoffmann, H.H.; Langley, D.R.; Meanwell, N.A.; Krystal, M.
“Inhibition of influenza virus replication via small molecules that induce
the formation of higher-order nucleoprotein oligomers.”
Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA (2011) Sep 13;108: 15366-15371
4 Protein Data Bank ID: 3RO5.
Crystal structure: influenza a H1N1 virus nucleoprotein with ligand (LGH)
NP Source: Influenza A/WSN/1933: H1N1
Authors: Pearce, B.C.; Edavettal,S.; McDonnell,P.A.; Lewis, H.A.; Steinbacher, S.;
Baldwin,E.T.; Langley, D.R.; Maskos, K.; Mörtl, M.; Kiefersauer, R.
Reference: Gerritz, S.W.; Cianci, C.; Kim, S.; Pearce, B.C.; Deminie, C.;
Discotto, L.; McAuliffe, B.; Minassian, B.F.; Shi,S.; Zhu, S.; Zhai, W.;
Pendri, A.; Li, G.; Poss, M.A.; Edavettal, S.; McDonnell, P.A.; Lewis, H.A.;
Maskos, K.; Mörtl, M.; Kiefersauer, R.; Steinbacher, S.; Baldwin, E.T.; Metzler, W.;
Bryson, J.; Healy, M.D.; Philip, T.; Zoeckler, M.; Schartman, R.; Sinz, M.;
Leyva-Grado, V.H.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Langley, D.R.; Meanwell, N.A.; Krystal, M.
“Inhibition of influenza virus replication via small molecules that induce
the formation of higher-order nucleoprotein oligomers.”
Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA (2011) Sep 13;108: 15366-15371
5 Protein Data Bank ID: 4DYA.
Crystal structure: WSN/A influenza nucleoprotein with BMS-885986 ligand bound
NP Source: Influenza A/WSN/1933: H1N1
Authors: Lewis, H.A.; Baldwin, E.T.; Steinbacher, S.; Maskos, K.; Mörtl, M.;
Kiefersauer, R.; Edavettal,S.; McDonnell, P.A.; Pearce, B.C.; Langley, D.R.;
“Crystal structure of WSN/A influenza nucleoprotein with BMS-885986 ligand bound”
Reference: To Be Published.
6 Protein Data Bank ID: 4DYB.
Crystal structure: WSN/A influenza nucleoprotein with BMS-883559 ligand bound
NP Source: Influenza A/WSN/1933: H1N1
Authors: Lewis, H.A.; Baldwin, E.T.; Steinbacher, S.; Maskos, K.; Mörtl, M.;
Kiefersauer, R.; Edavettal,S.; McDonnell, P.A.; Pearce, B.C.; Langley, D.R.;
“Crystal structure of WSN/A influenza nucleoprotein with BMS-883559 ligand bound”
Reference: To Be Published.
7 Protein Data Bank ID: 4DYN.
Crystal structure: WSN/A influenza nucleoprotein with BMS-885838 ligand bound
NP Source: Influenza A/WSN/1933: H1N1
Authors: Lewis, H.A.; Baldwin, E.T.; Steinbacher, S.; Maskos, K.; Mörtl, M.;
Kiefersauer, R.; Edavettal,S.; McDonnell, P.A.; Pearce, B.C.; Langley, D.R.;
“Crystal structure of WSN/A influenza nucleoprotein with BMS-885838 ligand bound”
Reference: To Be Published.
8 Protein Data Bank ID: 4DYP.
Crystal structure: WSN/A influenza nucleoprotein with BMS-831780 ligand bound
NP Source: Influenza A/WSN/1933: H1N1
Authors: Lewis, H.A.; Baldwin, E.T.; Steinbacher, S.; Maskos, K.; Mörtl, M.;
Kiefersauer, R.; Edavettal,S.; McDonnell, P.A.; Pearce, B.C.; Langley, D.R.;
“Crystal structure of WSN/A influenza nucleoprotein with BMS-831780 ligand bound”
Reference: To Be Published.
9 Protein Data Bank ID: 3ZDP.
Crystal structure: R416a Monomeric nucleoprotein of influenza A virus
NP Source: Influenza A/WSN/1933: H1N1
Authors: Chenavas, S.; Ruigrok; R.W.H.; Crépin,T.
Reference: Chenavas, S.; Estrozi, L.F.; Slama-Schwok, A.; Delmas, B.;
Di Primo, C.; Baudin, F.; Li, X.; Crépin, T.; Ruigrok, R.W.H.;
“Monomeric nucleoprotein of influenza A virus.”
Plos Pathog. (2013) 9(3): 3275-3284