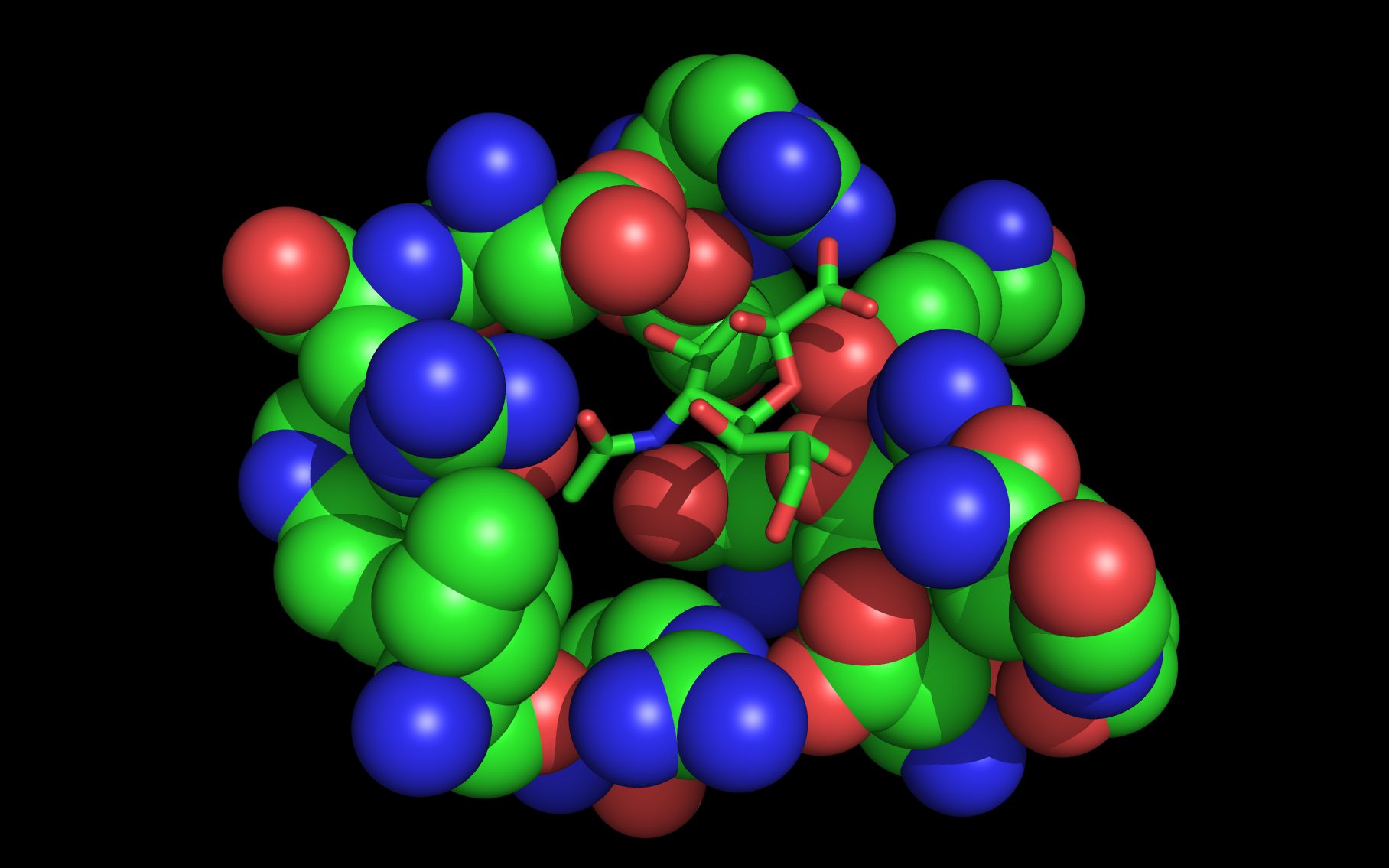
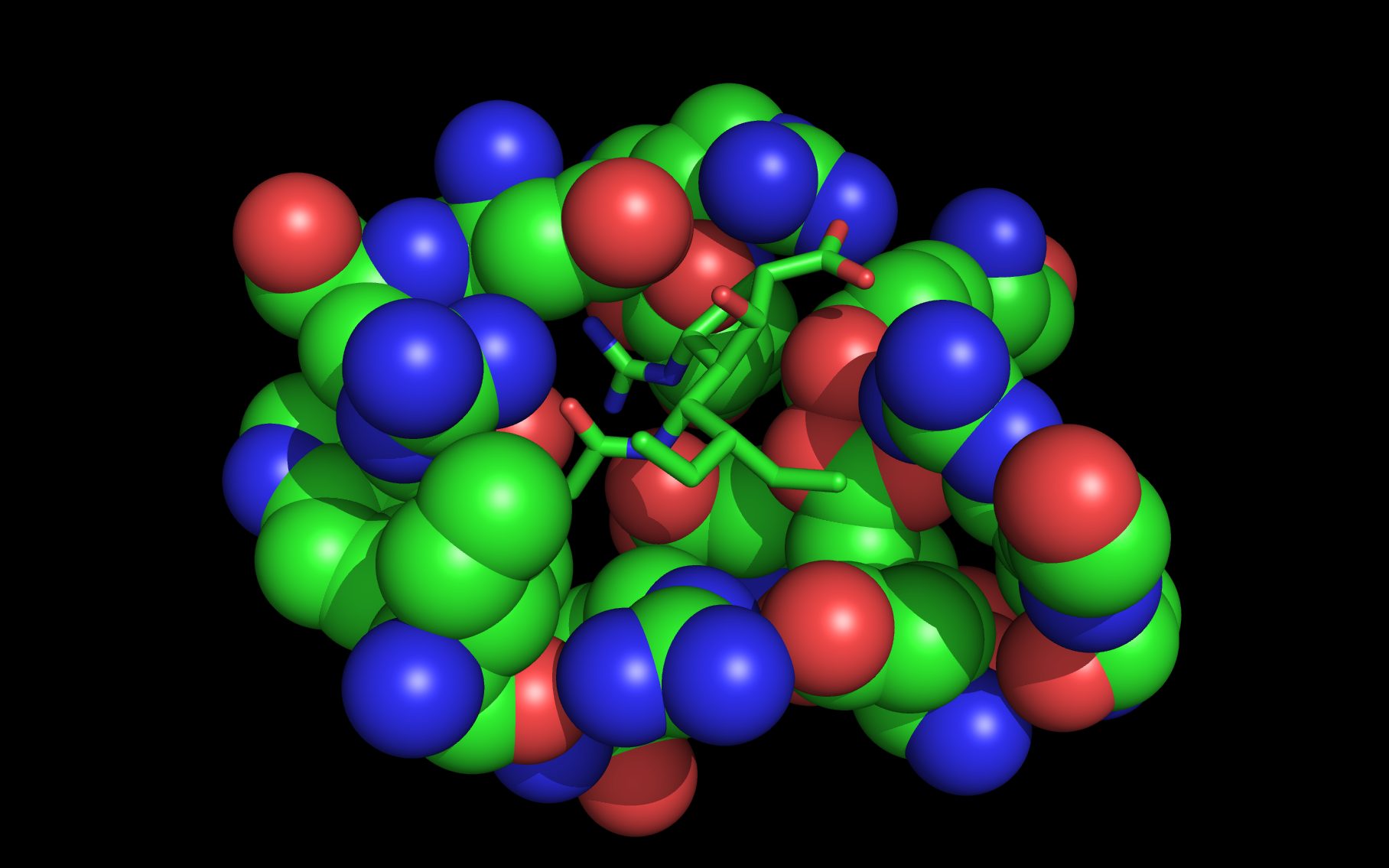
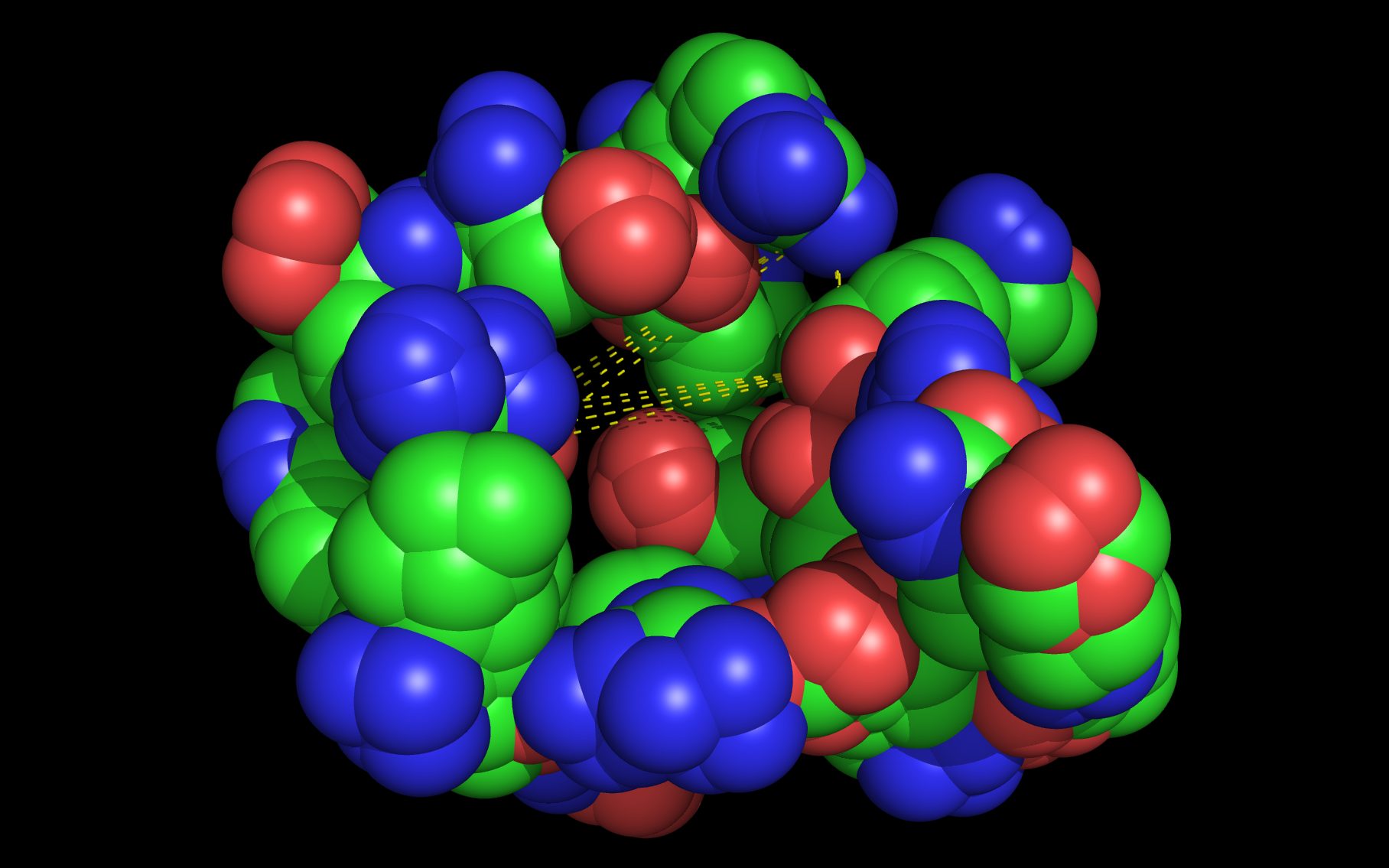
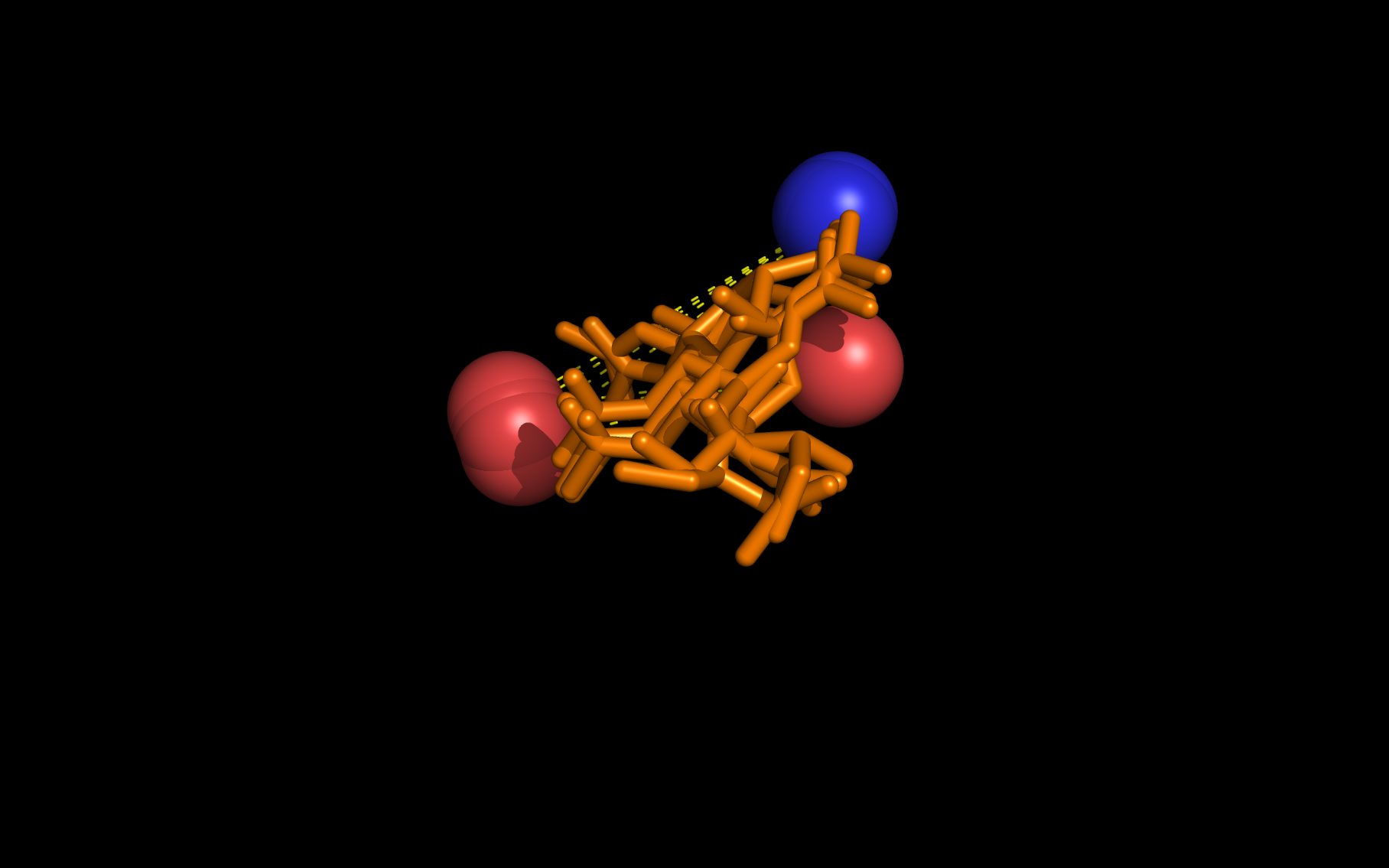
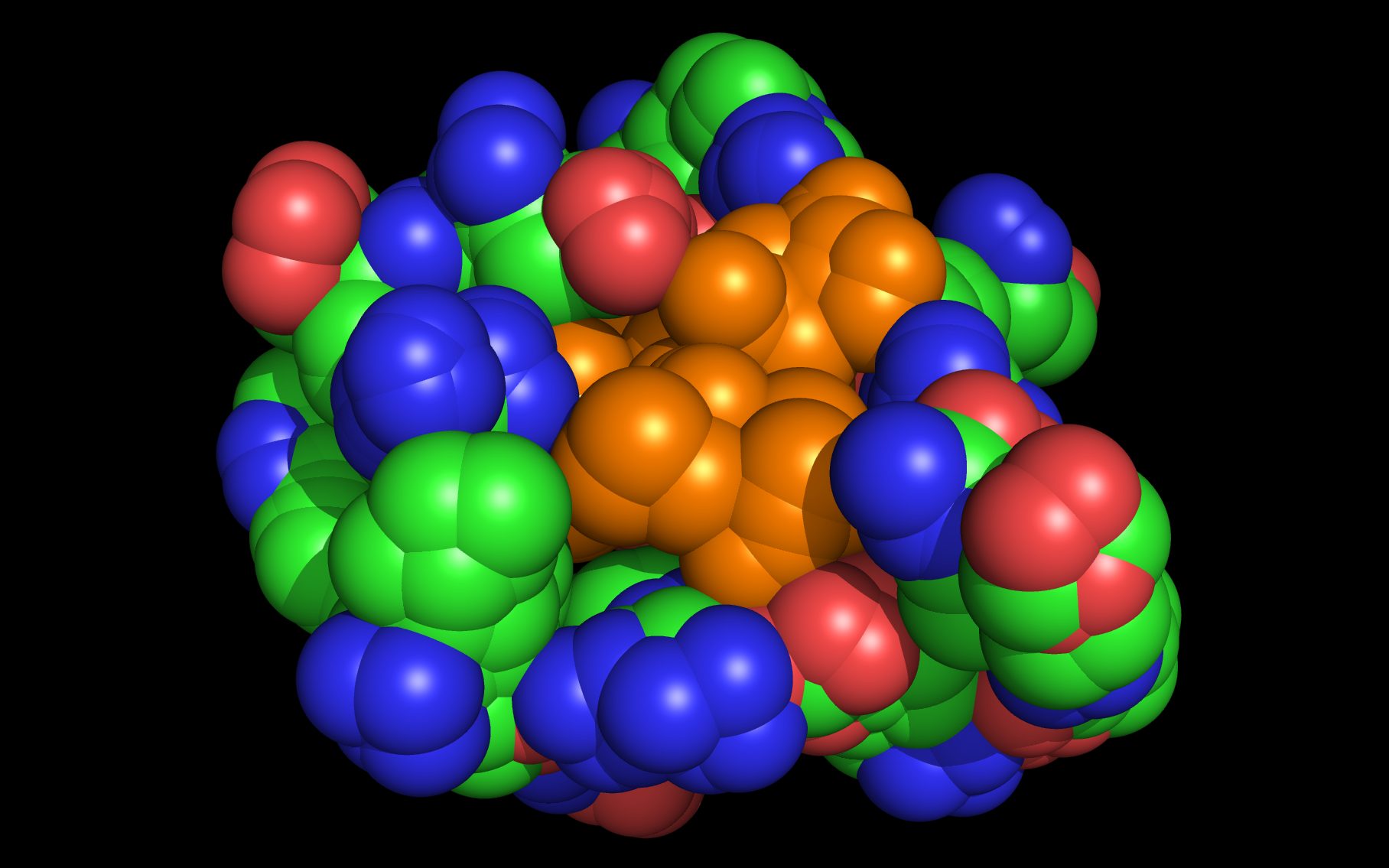
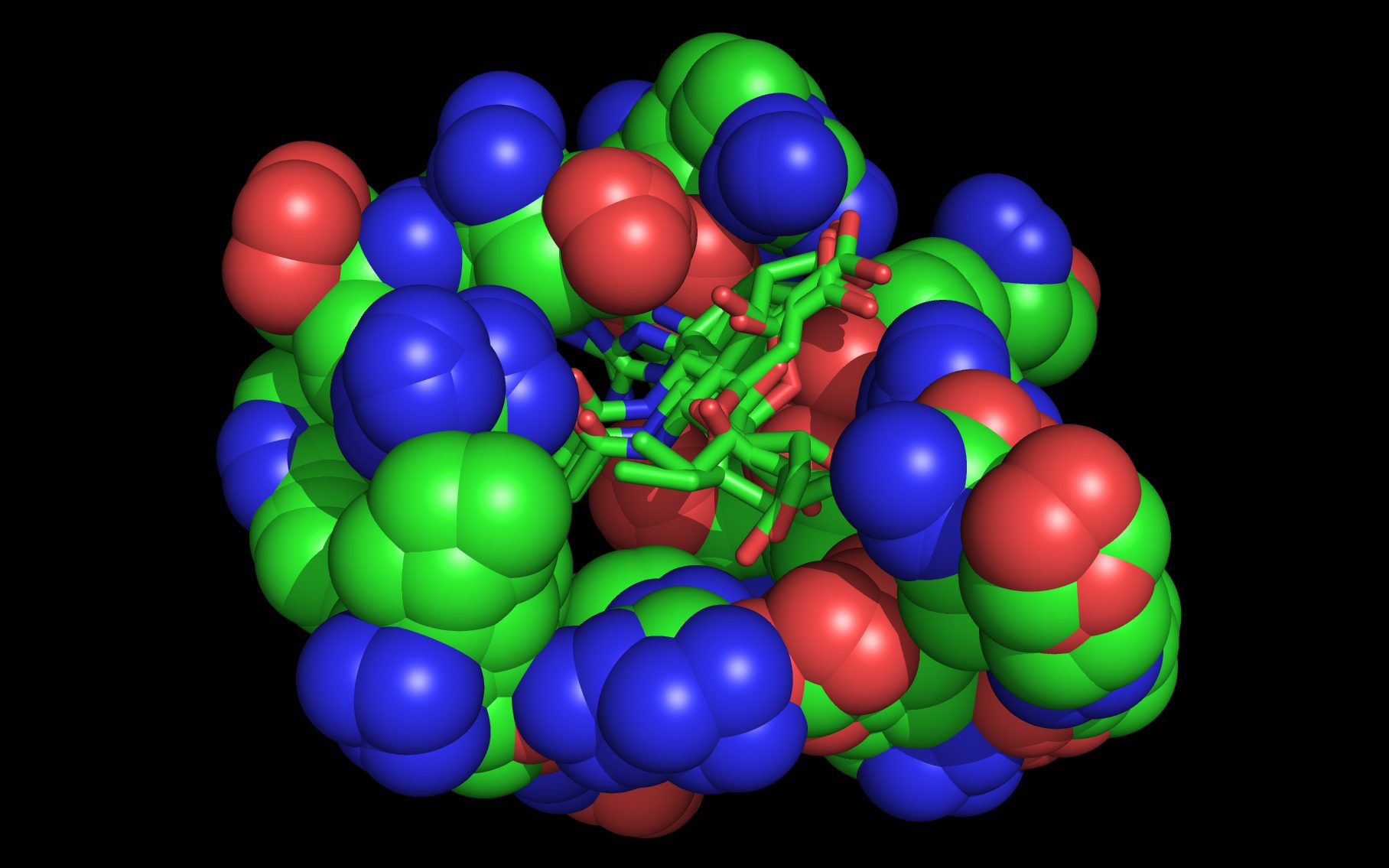
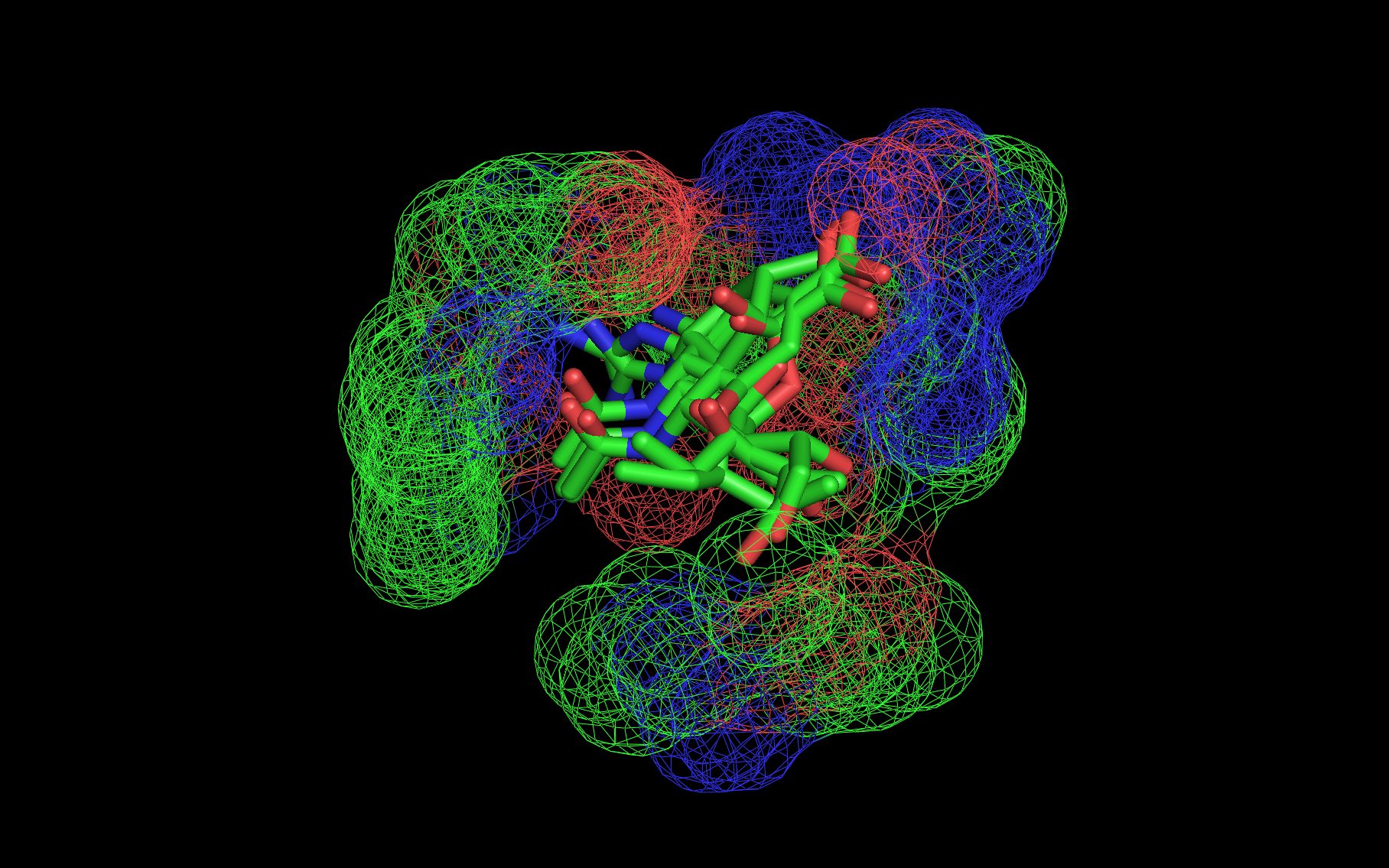
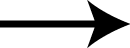Mouse over the small images above to change larger image and associated description. (Alternatively, read static PDF.)
In this example, one set of WWaveMarkers was derived from wwavePDB analysis of six closely related neuraminidase structures. 3B7E2 was used as the reference structure onto which the other neuraminidase structures were mapped. A seventh structure, 4FVK6, and an eight structure, 4GEZ7, were of a highly divergent N10 neuraminidase from a bat virus. The first set of WWaveMarkers could not be used with the N10 neuraminidase structures due to mutations of N10 neuraminidase residues whose atoms were in the first set of WWaveMarkers. A second set of WWaveMarkers was derived from the wwavePDB analysis of 4FVK6 and 4GEZ7 relative to the reference structure 3B7E2. The structures analyzed in this study were:
| 1W1X1 | neuraminidase subtype N6 in complex with sialic acid |
| 2HTU3 | neuraminidase subtype N8 in complex with peramivir (BioCryst) |
| 2HU43 | neuraminidase subtype N1 in complex with oseltamivir (Roche) |
| 3B7E2 | neuraminidase subtype N1 (1918 a/brevig) in complex with zanamivir (GSK) |
| 2QWA4 | neuraminidase subtype N9 with R292K mutation |
| 1A145 | neuraminidase subtype N9 with engineered VH and VL antibody domains bound |
| 4FVK6 | neuraminidase subtype N10 with divergent sequence |
| 4GEZ7 | neuraminidase subtype N10 with divergent sequence |
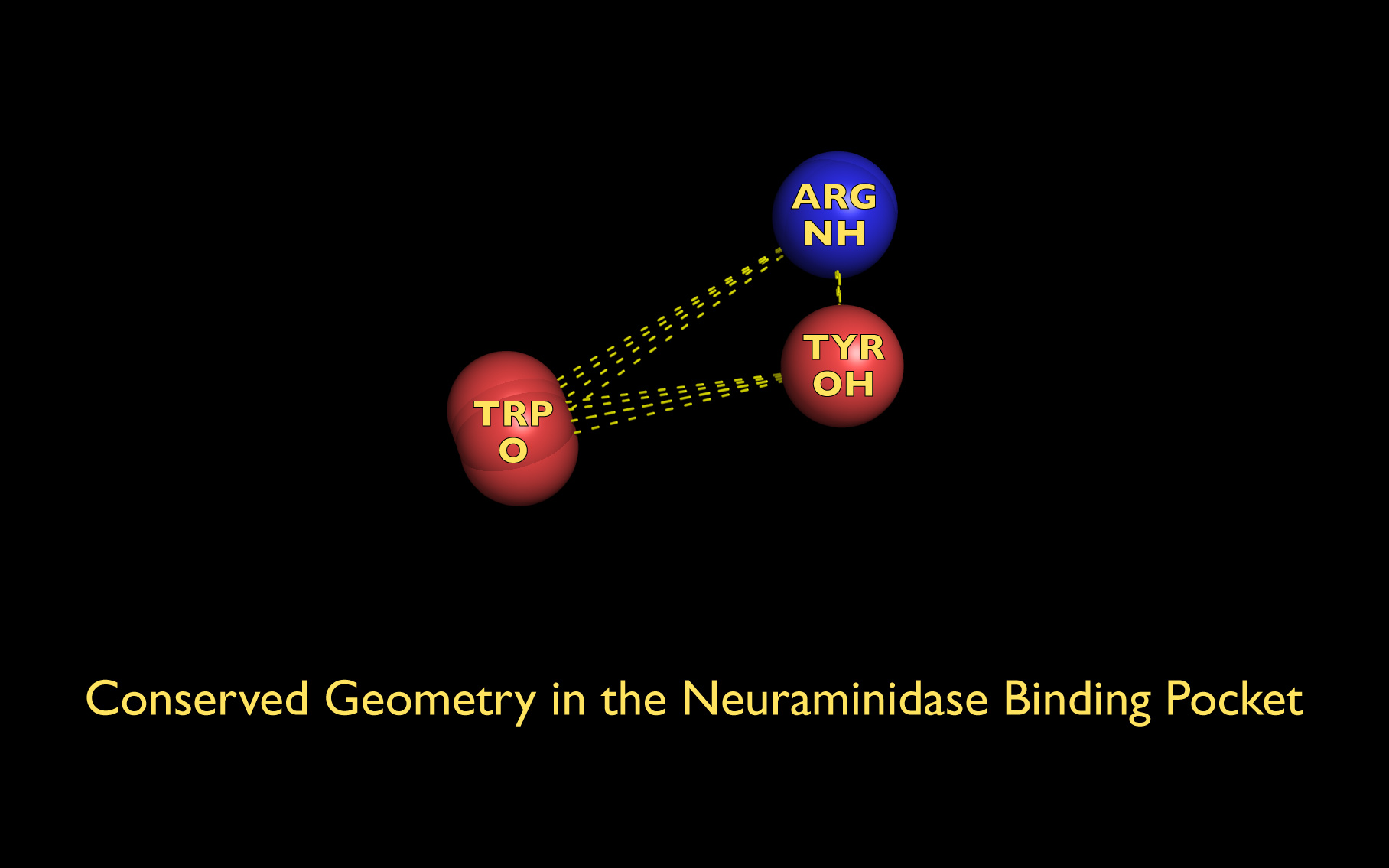
The first set of neuraminidase WWaveMarkers (atom serial # - residue - residue #) were:
| PDB | NH | O | OH |
| 3B7E | #269 ARG 118 | #744 TRP 178 | #2468 TYR 406 |
| 1W1X | #3308 ARG 1124 | #3779 TRP 1185 | #5497 TYR 1412 |
| 2HTU | #279 ARG 118 | #753 TRP 180 | #2489 TYR 411 |
| 2HU4 | #270 ARG 118 | #741 TRP 178 | #2458 TYR 406 |
| 2QWA | #269 ARG 118 | #744 TRP 178 | #2531 TYR 406 |
| 1A14 | #296 ARG 118 | #774 TRP 178 | #2533 TYR 406 |
The distances (D, in Angstroms) between the first set of neuraminidase WWaveMarkers are:
| PDB | D( O ↔ NH ) | D( O ↔ OH ) | D( NH ↔ OH ) |
| 3B7E | 744 ↔ 269: 9.706 | 744 ↔ 2468: 8.834 | 269 ↔ 2468: 4.321 |
| 1W1X | 3779 ↔ 3308: 9.961 | 3779 ↔ 5497: 8.654 | 3308 ↔ 5497: 4.267 |
| 2HTU | 753 ↔ 279: 9.987 | 753 ↔ 2489: 8.617 | 279 ↔ 2489: 4.552 |
| 2HU4 | 741 ↔ 270: 9.732 | 741 ↔ 2458: 8.735 | 270 ↔ 2458: 4.329 |
| 2QWA | 744 ↔ 269: 9.919 | 744 ↔ 2531: 8.464 | 269 ↔ 2531: 4.261 |
| 1A14 | 774 ↔ 269: 10.558 | 774 ↔ 2533: 8.587 | 269 ↔ 2533: 4.773 |
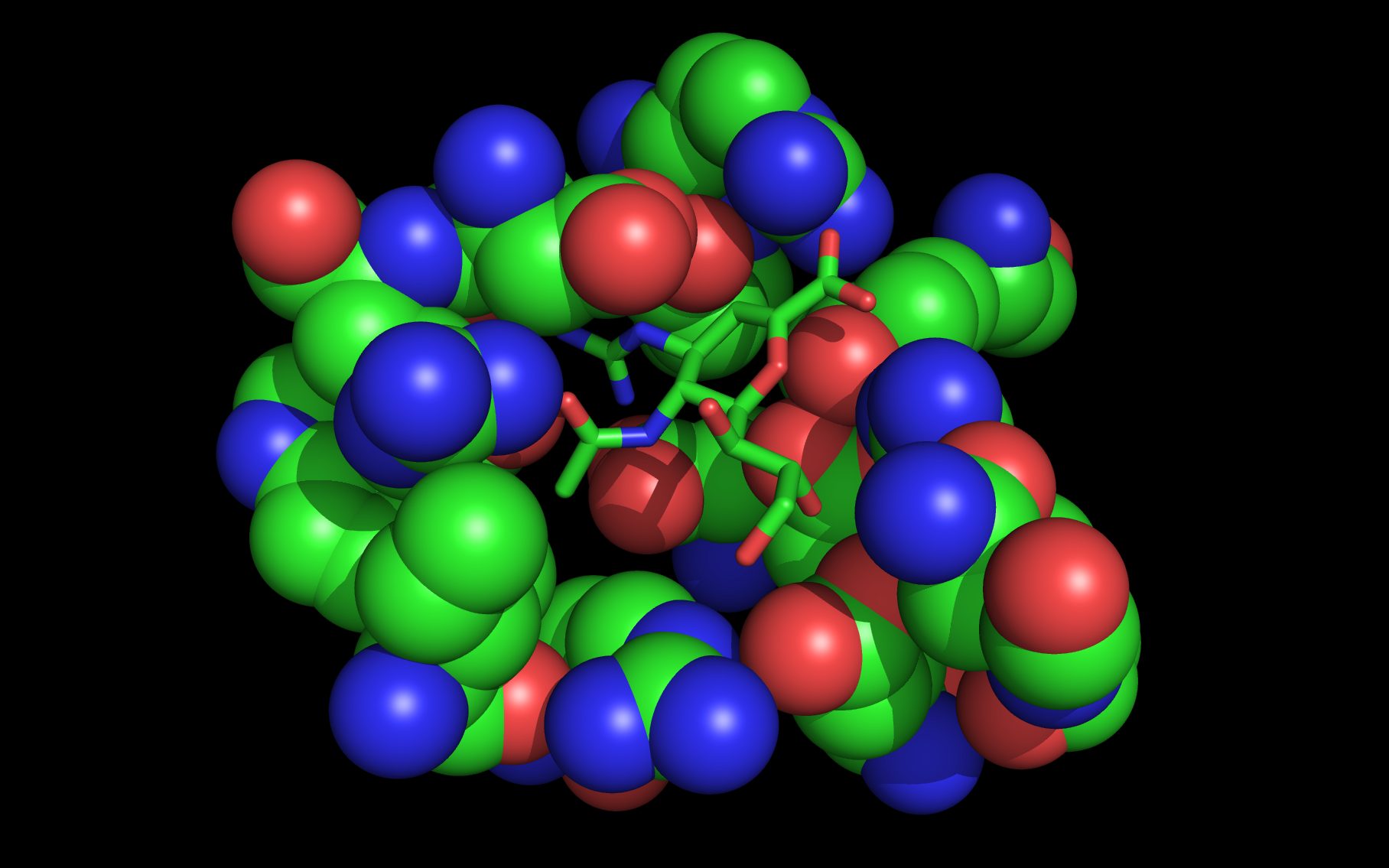
The first set of neuraminidase WWaveMarkers are shown in the image above color coded according to element ( N O ).
The second set of neuraminidase WWaveMarkers (atom serial # - residue - residue #) were:
| PDB | O | O | O |
| 3B7E | #262 ARG 118 | #1089 ARG 224 | #1487 GLU 276 |
| 4FVK | #3169 ARG 118 | #3974 ARG 224 | #4385 GLU 276 |
| 4GEZ | #8859 ARG 111 | #9664 ARG 215 | #10075 GLU 267 |
The distances (D, in Angstroms) between the second set of neuraminidase WWaveMarkers are:
| PDB | D( O ↔ O ) | D( O ↔ O ) | D( O ↔ O ) |
| 3B7E | 262 ↔ 1089: 14.730 | 262 ↔ 1487: 15.001 | 1089 ↔ 1487: 8.332 |
| 4FVK | 3169 ↔ 3974: 14.197 | 3169 ↔ 4385: 15.190 | 3974 ↔ 4385: 8.793 |
| 4GEZ | 8859 ↔ 9664: 14.178 | 8859 ↔ 10075: 15.353 | 9664 ↔ 10075: 8.924 |
Neuraminidase binding compounds
(The highlighted colors of the following SMILES match structures on the neuraminidase binding compounds page)
sialic acid (also named “SIA”)
IUPAC Name: (2R,4S,5R,6R)-5-acetamido-2,4-dihydroxy-6
-[(1R,2R)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl]oxane-2-carboxylic acid
SMILES: CC(=O)N[C@H]1[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO)O[C@](C(=O)O)(O)C[C@@H]1O
MUNANA (also named “MUS”)
IUPAC Name: (2S,4S,5R,6R)-5-acetamido-4-hydroxy-2
-(4-methyl-2-oxochromen-7-yl)oxy-6
-[(1R,2R)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl]oxane-2-carboxylic acid
SMILES: CC(=O)N[C@H]1[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO)O[C@H](C(=O)O)
(Oc2cc3oc(=O)cc(C)c3cc2)C[C@@H]1O
KDN
IUPAC Name: (2S,4S,5R,6R)-2,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[(1R,2R)
-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl]oxane-2-carboxylic acid
SMILES: O[C@H]1[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO)O[C@](O)(C(=O)O)C[C@@H]1O
zanamivir (also named “ZMR”)
IUPAC Name: (2R,3R,4S)-3-acetamido-4-(diaminomethylideneamino)
-2-[(1R,2R)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl]-3,4-dihydro-2H
-pyran-6-carboxylic acid
SMILES: CC(=O)N[C@H]1[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO)OC(C(=O)O)=C[C@@H]1N=C(N)N
oseltamivir (also named “G39”)
IUPAC Name: (3R,4R,5S)-4-acetamido-5-amino-3-pentan-3-yloxycyclohexene
-1-carboxylic acid
SMILES: CC(=O)N[C@H]1[C@H](OC(CC)CC)C=C(C(=O)O)C[C@@H]1N
peramivir (also named “BCZ”)
IUPAC Name: (1S,2S,3S,4R)-3-[(1S)-1-acetamido-2-ethylbutyl]
-4-(diaminomethylideneamino)
-2-hydroxycyclopentane-1-carboxylic acid
SMILES: CC(=O)NN[C@@H](C(CC)CC)[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](C(=O)O)C[C@H]1N=C(N)N
1 1W1X (neuraminidase complexed with sialic acid).
Rudino-Pinera, E.; Tunnah, P.; Crennell, S.J.; Webster, R.G.; Laver, W.G.; Garman, E.F.;
“The Crystal Structure Of Type A Influenza Virus Neuraminidase Of The N6 Subtype
Reveals The Existence Of Two Separate Neu5ac Binding Sites”
To Be Published/REVDAT 2H24-FEB-09 1W1X
2 Protein Data Bank ID: 3B7E (neuraminidase complexed with zanamivir).
Xu, X.; Zhu, X.; Dwek, R.A.; Stevens, J.; Wilson, I.A;
“Structural characterization of the 1918 influenza virus H1N1 neuraminidase.”
J. Virology (2008) 82: 10493-10501
3 2HTU (neuraminidase complexed with peramivir)
2HU4 (neuraminidase complexed with oseltamivir).
Russell, R.J.; Haire, L.F.; Stevens, D.J.; Collins, P.J.; Lin, Y.P.; Blackburn, G.M.;
Hay, A.J.; Gamblin, S.J.; Skehel, J.J.;
“The structure of H5N1 avian influenza neuraminidase suggests new opportunities
for drug design.”
Nature (2006) 443: 45-49
4 2QWA (R292K mutant neuraminidase).
Varghese, J.N.; Smith, P.W.; Sollis, S.L.; Blick, T.J.; Sahasrabudhe, A.;
McKimm-Breschkin, J.L.; Colman, P.M.;
“Drug design against a shifting target: a structural basis for resistance to
inhibitors in a variant of influenza virus neuraminidase.”
Structure (1998) 6: 735-746
5 1A14 (neuraminidase complexed with VH and CL antibody domains).
Malby, R.L.; McCoy, A.J.; Kortt, A.A.; Hudson, P.J.; Colman, P.M.;
“Three-dimensional structures of single-chain Fv-neuraminidase complexes.”
J.Mol.Biol. (1998) 279: 901-910
6 4FVK (divergent neuraminidase isolated from bats).
Li, Q.; Sun, X.M,; Li, Z.X.; Liu, Y.; Vavricka, C.J.; Qi, J.X.; Gao G.F.;
“Structural and functional characterization of neuraminidase-like molecule n10
derived from bat influenza a virus.”
Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA (2012) 109: 18897-18902
7 4GEZ (divergent neuraminidase isolated from bats).
Zhu, X.; Yang, H.; Guo, Z.; Yu, W.; Carney, P.J.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.M.; Paulson, J.C.;
Donis, R.O.; Tong, S.; Stevens, J.; Wilson, I.A.;
“Crystal structures of two subtype N10 neuraminidase-like proteins from bat
influenza A viruses reveal a diverged putative active site.
Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA (2012) 109: 18903-18908